Are you going to become a mom the first time? It’s quite normal- some anxiety and worries, nearing your due date! You must be wondering when your labor might start and what do different labor contractions feel like? What are different labor contractions known as? How could you cope with labor pain? How long labor contractions last with me?
Though there are many signs related to labor contractions, one of the most common signs is when you experience constant contractions in the uterus.
I’m writing this article on my own delivery experience, what do different labor contractions feel like?
What Do Different Labor Contractions Feel Like?
False Labor (Braxton-Hicks Contractions)
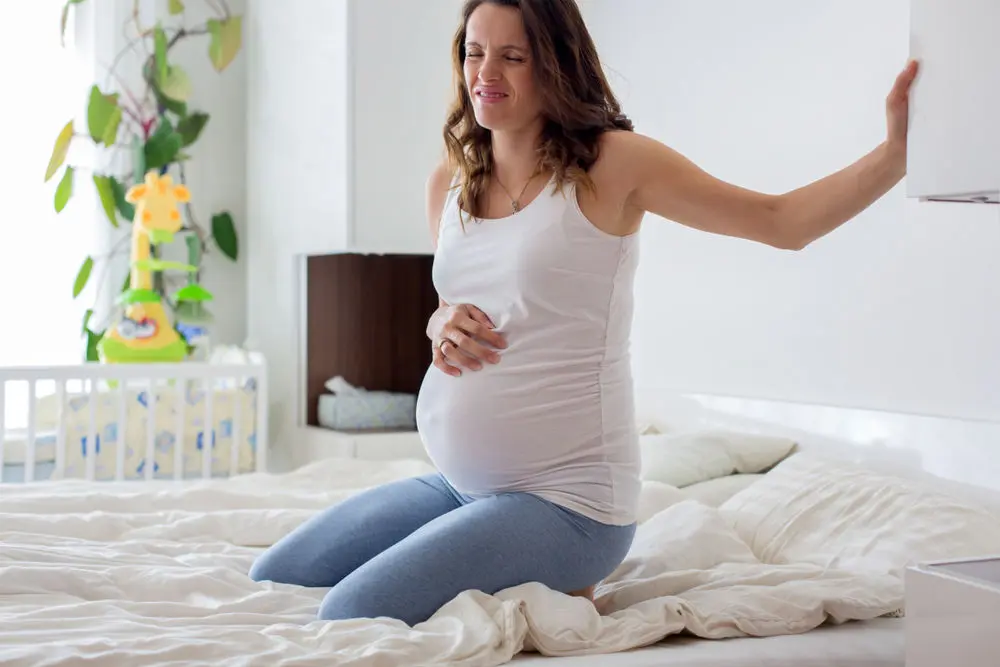

When you’ll complete the four months of pregnancy, you may start to feel your uterus contracting from time to time. This tightening is known as Braxton-Hicks contractions. You know this term originated in 1872 when an English doctor named John Braxton Hicks described the contraction exactly occur before real labor.
What Braxton Hicks Contractions feel like?
Earlier I told — these contractions begin after completing four months of pregnancy, A.K.A, start in the second trimester.
Now, what happens when these start? The muscles of your uterus tighten for approximately 30 to 50 seconds, or as long as for a minute.
You can name them- “practice contractions” Because these contractions help you prepare for the real event and allow you to practice the breathing exercise taught in the childbirth classes.
Braxton Hicks are described as:-
- Irregular in intensity
- infrequent
- Braxton hicks are not so painful
- These only poke you and disappear
- They make you uncomfortable than pain
- Non-rhythmic
Cause Braxton Hicks labor contractions:-
Some physicians and midwives believe that these contractions play a crucial part in intoning the uterine muscles and makes the flow of blood easier to the placenta. They also help to soften the cervix.
However, as Braxton hicks contractions will become intensive nearer the time of delivery, and referred to as ‘false labor’.
What triggers Braxton Hicks’s labor contractions?
- When someone touches the mother’s belly
- when the bladder is full
- After sex
- Dehydration
What to do to alleviate Braxton Hicks contraction?
- Change position: Lie down if you have been standing for a long time.
- Take a warm bath.
- Drink couples’ glasses of water to stay hydrated.
- drink a warm cup of milk or herbal tea.
But if nothing is working, you should contact your health care provider or midwife.

Back Labor: Causes, Complications, and Prevention
Back labor refers to the pain and discomfort a pregnant woman experiences during the laboring period. Mostly, soon-to-be-mom feels slight cramping in the lower back and many women complain about severe discomfort in the lower back which becomes intense during delivery time.
What causes Back Labor?
A frequent cause of back labor is the position of the baby in the uterus. When a baby faces the mother’s abdomen, it can cause the pressure of the baby’s head towards the mother’s sacrum(tailbone). But it is not always because of the baby’s odd position. There are many techniques that can be used to change the position of the baby.
Techniques to improve the position of the baby:-
- Walking
- Squatting and lunging
- Using a birth ball
Sitting backward on a chair or the toilet seat
Use these techniques to ease discomfort:-
- Apply cold or hot compresses on the lower back
- Strong counter-pressure
- Take a warm bath or birth pool
- Roll down the water bottle, or tennis ball with pressure down on the back
- Taking a childbirth class or having professional labor support by a doula can be beneficial.
Back labor can cause complications for the mother or the baby?
No, it doesn’t harm the baby or the mother. The main cause of back labor is an odd position of the baby in the mother’s womb(baby being head down and facing your tummy). For which a mother experiences difficulty descending through the birth canal.
One small study shows that women who have a higher body mass index(BMI) are more likely to have pain in the back
How you can prevent back labor:-
You can do these things to encourage your baby to get in the right position, head-down position:-
- Walking
- Squatting and lunging
- Sitting on a birth ball
- A hot or cold compress applied to the lower back
- Strong counter-pressure
- Take a warm bath or birth pool
- Heated rice sock
- Applying pressure of rolling such as water bottle, beverage can, tennis ball
- Taking a comprehensive childbirth class or support of a professional doula can be beneficial
A pregnant woman will not able to know if she experiences back labor. If a woman who had experienced it in the past is more likely to have back labor in the future unless preventative measures are taken.
Because back labor is caused due to baby’s position, steps can be taken to increase the chances of a favorable fetal position during pregnancy, with the help of your health provider or experienced doula are as below:-
- Do pelvic tilts-Get on your hands and knees, curl your back up and then resume the right position. This exercise helps to loosen the ligaments and provide relief from back pain.
- Spend some time of the day sitting on the birth ball/exercise ball.
- Avoid sitting for a long time on your couch or any recliner chair.
- Have a massage throughout your pregnancy.
- Regularly keep an eye on the baby’s position as the pregnancy progresses.
Preterm Labor Contractions
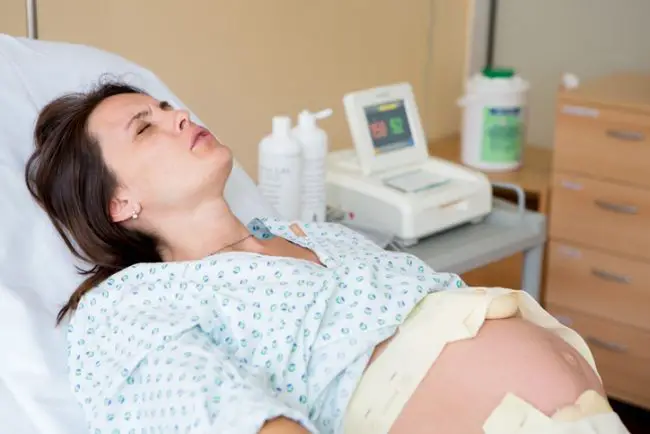
Premature labor also called preterm labor. These start when your body starts getting ready for the birth before the due date. It can lead to premature birth. But nothing to worry as the doctors can do a lot to delay the delivery.
Regular contractions before 38 weeks may be a sign of premature labor. The timing of regular contractions means they follow a regular pattern. It means if you’re getting contractions every ten minutes for over an hour, you may be in preterm labor.
During a contraction, your entire abdomen will get hard to touch with tightening in your uterus and you may feel:
- a dull backache
- pressure in your pelvis
- a kind of pressure in your abdomen
- cramping
These are a sight that alarm you and you should call your doctor if they are accompanied by vaginal bleeding, diarrhea, or a gush of watery discharge which maybe your water breaking.
Some risk factors associated with preterm labor are:-
- Multiple pregnancies (twins, triplets, etc)
- high-stress level
- certain infections
- being under or overweight before pregnancy
- not taking proper prenatal care
- Smoking
- Drinking alcohol or using any types of drugs during pregnancy
- being pregnant with twins
- A family or personal history of premature labor
- getting pregnant too soon after having a baby
It’s very important to pay attention to the duration and frequency of your contractions. You’ll need to provide all the information to your doctor. Your doctor provides you treatment or medicines to stop labor from progressing.
How to check for contractions
Checking contractions means a way of spotting early labor conditions:-
- Place your fingertips on your abdomen.
- If you feel uterus tightening and softening, that’s a contraction
- The note time duration of contraction starts and ends up
- Try to stop the contraction. Get off your feet, change your position, drink two or three glasses of water
Call your midwife or doctor if you are experiencing continue contraction every 10 minutes or more often if this condition gets worse or feel severe pain then don’t waste a single minute and get help o your doctor or midwife.

I love your writing! It’s true that you put a different spin on the English language than most but what you’re trying to convey is very clear,and has obvious intelligence, knowledge, and know-how. I’ve read a few of your articles now and I feel smarter, more empowered, and have had a few good laughs! Thanks for writing!
Glad Icould help.