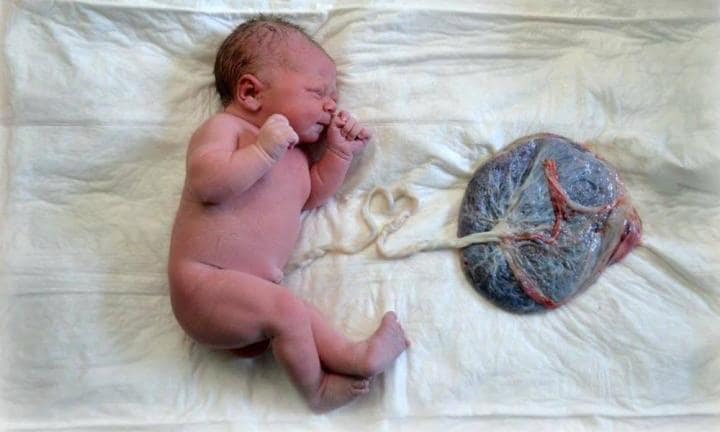
Benefits of delayed cord clamping
As soon as our baby is born, the umbilical cord that connect the baby with mother’s placenta, cut down immediately. Earlier it was a myth that the umbilical cord is a relic part and no longer needed for newborn life support. But today everyone knows the benefits of delayed cord clamping after birth process.
The American College of Nurse-Midwives endorse this document. This Committee Opinion was developed by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Committee on Obstetric Practice in collaboration with committee members Maria A. Mascola, MD; T. Flint Porter, MD; and Tamara Tin-May Chao, MD.the committee opinion was develop. The cord and placenta are the kind of external circulation system of our baby as one vein carries fresh oxygen and nutrients rich blood, from the placenta to the baby and the other two arteries carry carbon dioxide-rich blood and waste away from baby for purification.
So. allow to pulsate and transfer all necessary substances like billions of red blood cells, stem cells, white cells, oxygen and blood from the cord to the baby. These all are allowed to transition to life outside the uterus to your newborn as he becomes stable. It is a Delayed umbilical Cord Clamping.
Optimal Timing for Umbilical Cord Clamping:-
When your baby is born placenta and cord contains about 1/3 of blood in the placenta and the remaining 2/3 is with your baby through cord.
After birth cutting down cord immediately practiced for 50 -60 years ago but recent researches show that it is not good for the baby. Because newborn miss out a large amount of blood unnecessarily after lossing cord blood.
In the modern age, World Health Organization led to more changes and guidelines to practice towards delayed umbilical cord clamping. The new guideline is, late cord clamping until the cord has stopped pulsating and becomes white.
It is increasing as a regular practice in births even where no medical facilities available.
Even in the lack of medical facilities usually, the midwife should be able to feel by just touching to the cord. If there is a reason not to wait for the time, then also they should wait at least 1 – 3 minutes following the birth of the newborn before cutting the cord.
Future research
The optimal timing of umbilical cord clamps needs to be determined. It will likely provide an effective way for preterm infants care in placental emergencies and is often more difficult unless there will still be a need for rapid intervention.
Currently, it is considered a question about whether it will work in beds without intubated placenta circulation in babies. The optimum timing of maternal and neonatal outcomes with use of ureterotonic agents in pregnancy needs further investigation. Several areas require further study in this regard as possible effects on immediate and long-term immunity against disease.
What Does World Health Organization Research Say?
Delyaed umbilical cord clamping improves maternal bleeding and infants nutritious health.
According to World Health Organization Babies who have delayed cord clamping in a few minutes after their birth having more skill than preterm infants whose cords cut down immediately after birth.
Obstetrician and gynocologists recommended the cord clamping is delayed in all birth centers for at least 1 -5 minutes in all newborns.
If the fetal heart is less than 60 bpm and not getting faster, if this is the reason, then the only preterm babies may need to take away to get breathing support.
Umbilical Cord Milking increases blood volume and flow in preterm infants.
“The study results are very encouraging,” said Tonse Raju, M.D., chief of NICHD’s Pregnancy and Perinatology Branch. “The findings need to be confirmed in a larger number of births, but at this point, it appears that umbilical cord milking may prove to be of great benefit to preterm infants delivered via cesarean.”
How long delayed umbilical cord clamping should be delayed?
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) says that the cord should be delayed for at least 30-60 seconds.
The World Health Organisation recommends clamping the umbilical cord for 1 minute or until the cord has stopped pulsing.
Ideally, it should have waited until the umbilical cord is wholly drained, limp and changes in white color.
- For 1-minute wait, baby gets 50% of the cord blood
- For 3 minutes wait, baby gets 90% of the cord blood
5 minutes wait and baby could get all of the necessary fluids through delayed cord clamping. It improves infant health.
There are no EXACT times that may vary from one baby to another, So, the best time is, clamp the umbilical cord when it stops pulsing and begins to limps, finally becomes white.
7 Benefits of Delayed umbilical cord clamping
1. It Lower risk of anemia rate
Delayed umbilical cord clamping naturally supplies baby with iron, as iron plays a vital for life and the proper development of infants. Because soon after birth recent breastmilk is insufficient in iron.
As soon-be-mama needs iron to rebuild and nourish her body after birth. So the baby doesn’t get enough iron with breastfeeding. But if the baby is benefited with delayed cord clamping, he gets all the necessary substances with it.
It is researched that anemic mothers also benefited from delayed umbilical cord clamping. The delay improved iron stores and hemoglobin levels in babies born to anemic mothers.
Delayed cord clamping provides a lot of influx of iron-rich blood cells until the cord is pulsating.
Some researches declare that the stem cells received during delayed umbilical cord clamping are essential to repairs damaged cells. It’s crucial for immune functions effectively throughout the entire life of a person.
Babies who don’t get umbilical cord blood becomes anemic at four months of age, as they will not gain access to the part of their blood which itself in the placenta.
2. Benefits of the extra blood of the placenta
The extra blood in the placenta will save a baby from anemia and iron deficiency during his first years of life. The extra blood through delayed cord clamping increases baby’s iron storage which is essential for healthy brain development.
If baby’s umbilical cord cut immediately he misses out of that iron infusion and he may be struggling with anemia in his recent years of childhood.
If they immediately cut the cord down they can negatively fluctuate down some excellent motor skills as well as social skills (Coordinating small muscles, such as hands and fingers) at the age of four to five years
But if they have delayed umbilical cord clamping for at least 3 minutes after birth, the rates of social skills are higher and generate excellent motor skills than those who had immediate CC.
Additional Benefits of Delayed Cord Clamping
Besides the benefits which come with the adequate iron for the babies, it also has a smoother cardiopulmonary transition at birth.
Another potential benefit of the Delayed umbilical cord clamping is to ensure that the baby can receive an increased volume of blood. It will naturally increase the blood platelet which is needed for blood clotting.
Stem cells are increased:-
Delayed umbilical cord clamping results in an infusion of stem cells, which plays a vital role in the development of the immune system, respiratory, cardiovascular, and nervous system.
So many beneficial internal functions take place with delayed cord clamping. If a baby has a severe birth problem then with Delayed umbilical Cord Clamping, stem cells can help the baby to repair any brain damage during hard birth.
3. Cord clamping for a premature baby
Delayed umbilical cord clamping is the blessing for premature infants as they are born underweight. Premature babies get lots of benefits with DCC:
- Stabilized Blood Pressure
- The higher amount of red blood cells
- They don’t rely on ventilation and oxygen for many days.
- They need less blood transfusion
- Lower risk of hemorrhage
- They have a lower risk of any infection
- They have a lower risk of anemia
If you know your pregnancy status and having the risk of a premature baby. Then definitely, you have to put delayed cord clamping on your birth plan and discuss it with your birth team.
4. Delay clamping and Cesarean section
Delayed clamping can still be applied if there is a cesarean section, whether you have planned or an emergency.
It is becoming a common practice in almost all birth centers. The world has come close to the wonders of delay cord clamping.
40-seconds delayed clamping provides the infant with a partial placental transfusion. Another approach at the time of C-section delivery is to milk the umbilical cord where time and speed are important factors.
So, if you have a c-section even than you can add DCC in your birth plan, which will give you an opportunity to talk about DCC and your infant will also get benefits from DCC.
Is DCC increasing the risk of jaundice to a newborn?
Are there any disadvantages to delayed cord clamping?
Jaundis comes about when babies can’t quickly take down their red-cells, which means that there has been no significant reduction in the number and quality of red cells in the brain. A delayed cord clamping will allow more blood to flow through the infant. Baby babies have a greater chance of breathing problems and will require immediate emergency care. Tell me more about milking the umbilical cord by manually pulling blood into the cord during the last two minutes. The evidence indicates the drug will not cause damage, but will be effective for people with premature jaundice. When you had a healthy baby, but had a pregnancy you’d never consider cutting cords at the newborn.
Myths about delayed cord clamping after birth!
Some studies have shown that delayed clamping can slightly increase the chance of jaundice in the newborn but strong evidence shows that the benefits of delayed clamping outweigh this.
Jaundice is very common in newborns, however, only a few babies may need phototherapy to help get rid of jaundice no matter when the cord blood was clamped.
Only a smaller spectrum covers these myths with the truth…Some studies show that delaying in cord clamping about 5% of babies required treatment for jaundice compared to 3% of babies who had early cord clamping.
5. Injection to deliver the placenta
Of course yes, if you have injection it usually takes 5-10 minutes before the placenta is delivered and your cord remains intact allowing for the transfer of the blood to your baby.
6. When should we not apply umbilical cold clamping?
Mostly, umbilical cord blood is beneficial in all aspects. However, there are a few circumstances which may be not suitable such as:-
- If the soon-to-be-mama has heavy bleeding after birth.
- If there is an issue with the placenta or if the cord is bleeding.
- Even If the baby has an issue of breathing, the umbilical cord may need to be cut immediately.
7. What is the placental transfusion?
The placenta is an organ that develops in mammal’s uterus during pregnancy which helps to nourish and to maintain the baby inside the womb through the umbilical cord.
It is attached to the wall of the mother’s uterus and the baby’s umbilical cord arises from it.
Inside the uterus placenta and umbilical cord provide the baby with oxygen, nutrients and clear his waste.
As fetal life, the baby needs a small amount of blood and the placenta plays an essential role in the lung, kidneys, gut, and liver for the baby. Baby’s total blood volume is present in the placenta only.
So, the cord blood circulating in the placenta is not extra or waste blood it belongs to the baby.
Even after birth, the cord pulsates and the placenta continuing to provide oxygen, nutrients, and blood back to the baby.
This type of blood is called placental transfusion and it is pretty, necessary for the newborn.
The placental transfusion is the system that provides a baby with red blood cells, and blood volume.
Risk of immediate cord clamping
Various studies have shown that immediate cord clamping can damage physiology, anatomy, and the birth process.
Clinical trials in premature infants
One-month long hematopically clamped cords were used to clamp the cords between newborn fetus in the first 24 yr gestation in the first 18 yr. 1. Delaying cord clamps caused a lower number of babies who need blood transfusions for anemia. It was much less likely ventricular hemorrhalgae (ultrasonographic diagnostics — e.g. the all-types) in addition to necromizing entercolitis. Peak bilirubin is found largely at birth with the infant group. For onset of neonatal death serious (grade 3–3) hemorrhage or periventricular leukemia: no.
Side effects of delayed clamiping
Delay cord clamping severs the baby from the still functioning placenta and halts the blood circulations.
It may lead to the lower iron stores in the baby for up to 6 months after birth. Iron deficiency in the first few months of life is irreversible.
Delaying cord clamping create complications for the mother, too. umbilical cord immediately increases the risk of postpartum hemorrhage.
It decreases the blood flow within the umbilical cord of the newborn. It may create difficulty for the uterus to contract and expel the placenta.
Recommendations
Committees in Obstetrics made these recommendations by the American Society for Obstetrics. Delayed umbilical cord locking has significant neonatal outcomes in early-onset infants: improvement of fetal vascular stability, vascular efficiency, improved red blood cells count, reduction in transfusion and less infection by inflammatory. There have been some increases to numbness after babies have experienced delayed cord clamping. Generally speaking the American College recommends stopping clamping umbilical cords at birth by 60 seconds and preventing premature death in newborn children.
Conclusion:-
Premature babies born with iron deficiency anaemia and DCC leaves with the baby after birth and avoids disturbing the normal birth process.
The cord pulsating and placental transfusion improved maternal health. Plus supplying the oxygenated blood, nutrients, blood rich in iron, red blood cells, stem cells, and immune cells is necessary for healthy infants.
Delayed cord clamping is a blessing for the children who take birth in a premature stage and is helpful in better motor development.
DCC provides these children to survive easily with all life-supporting essential substances by restoring blood volume and protects them against any damage, brain injury, or even death.
I hope you understood what benefits delaying the cord clamping brings to you. Soon-to-be-mamas, don’t fret, it is for your baby, all-natural. And my sweet moms out there who have opted for DCC, do share your story in the comment section and encourage other moms, until then
TAKE CARE!